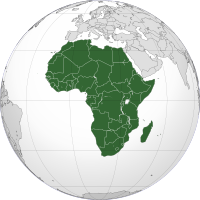
 Africa Africa | |
| Area | 30,221,532 km2 (11,668,599 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 1,022,234,000[1] (2010, 2nd) |
| Pop. density | 30.51/km2 (about 80/sq mi) |
| Demonym | African |
| Countries | 56 (list of countries) |
| Dependencies | List |
| Languages | Languages of Africa |
| Time Zones | UTC-1 to UTC+4 |
| Largest cities | List of metropolitan areas in Africa List of cities in Africa |
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² (11.7 million sq mi) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area.[2] With 1.0 billion people (as of 2009, see table) in 65 territories (including 54 recognized states), it accounts for about 14.72% of the world's human population.
The continent is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, both the Suez Canal and the Red Sea along the Sinai Peninsula to the northeast, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The continent includes Madagascar and various archipelagoes and has 54 sovereign states ("countries") and two states with limited recognition.
Africa, particularly central Eastern Africa, is widely regarded within the scientific community to be the origin of humans and the Hominidae clade (great apes), as evidenced by the discovery of the earliest hominids and their ancestors, as well as later ones that have been dated to around seven million years ago – including Sahelanthropus tchadensis, Australopithecus africanus, A. afarensis, Homo erectus, H. habilis and H. ergaster – with the earliest Homo sapiens (modern human) found in Ethiopia being dated to circa 200,000 years ago.[3]
Africa straddles the equator and encompasses numerous climate areas; it is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate to southern temperate zones.[4] The African expected economic growth rate is at about 5.0% for 2010 and 5.5% in 2011.[5]
Afri was a Latin name used to refer to the Carthaginians who dwelt in North Africa in modern-day Tunisia. Their name is usually connected with Phoenician afar, "dust", but a 1981 hypothesis[6] has asserted that it stems from the Berber word ifri or ifran meaning "cave" and "caves", in reference to cave dwellers.[7] Africa or Ifri or Afer[7] is the name of Banu Ifran from Algeria and Tripolitania (Berber Tribe of Yafran).[8]
Under Roman rule, Carthage became the capital of Africa Province, which also included the coastal part of modern Libya.[9] The Latin suffix "-ica" can sometimes be used to denote a land (e.g., in Celtica from Celtes, as used by Julius Caesar). The later Muslim kingdom of Ifriqiya, modern-day Tunisia, also preserved a form of the name.
Other etymological hypotheses that have been postulated for the ancient name "Africa":
 At the beginning of the Mesozoic Era, Africa was joined with Earth's other continents in Pangaea.[11] Africa shared the supercontinent's relatively uniform fauna, which was dominated by theropods, prosauropods and primitive ornithischians by the close of the Triassic period.[11] Late Triassic fossils are found through-out Africa, but are more common in the south than north.[11] The boundary separating the Triassic and Jurassic marks the advent of an extinction event with global impact, although African strata from this time period have not been thoroughly studied.[11]
At the beginning of the Mesozoic Era, Africa was joined with Earth's other continents in Pangaea.[11] Africa shared the supercontinent's relatively uniform fauna, which was dominated by theropods, prosauropods and primitive ornithischians by the close of the Triassic period.[11] Late Triassic fossils are found through-out Africa, but are more common in the south than north.[11] The boundary separating the Triassic and Jurassic marks the advent of an extinction event with global impact, although African strata from this time period have not been thoroughly studied.[11]
Early Jurassic strata are distributed in a similar fashion to Late Triassic beds, with more common outcrops in the south and less common fossil beds which are predominated by tracks to the north.[11] As the Jurassic proceeded, larger and more iconic groups of dinosaurs like sauropods and ornithopods proliferated in Africa.[11] Middle Jurassic strata are neither well represented nor well studied in Africa.[11] Late Jurassic strata are also poorly represented apart from the spectacular Tendaguru fauna in Tanzania.[11] The Late Jurassic life of Tendaguru is very similar to that found in western North America's Morrison Formation.[11]
Midway through the Mesozoic, about 150–160 million years ago, Madagascar separated from Africa, although it remained connected to India and the rest of the Gondwanan landmasses.[11] Fossils from Madagascar include abelisaurs and titanosaurs.[11]
 Later into the Early Cretaceous epoch, the India-Madagascar landmass separated from the rest of Gondwana.[11] By the Late Cretaceous, Madagascar and India had permanently split ways and continued until later reaching their modern configurations.[11]
Later into the Early Cretaceous epoch, the India-Madagascar landmass separated from the rest of Gondwana.[11] By the Late Cretaceous, Madagascar and India had permanently split ways and continued until later reaching their modern configurations.[11]
By contrast to Madagascar, mainland Africa was relatively stable in position through-out the Mesozoic.[11] Despite the stable position, major changes occurred to its relation to other landmasses as the remains of Pangea continued to break apart.[11] By the beginning of the Late Cretaceous epoch South America had split off from Africa, completing the southern half of the Atlantic Ocean.[11] This event had a profound effect on global climate by altering ocean currents.[11]
During the Cretaceous, Africa was populated by allosauroids and spinosaurids, including the largest known carnivorous dinosaurs.[11] Titanosaurs were significant herbivores in its ancient ecosystems.[11] Cretaceous sites are more common than Jurassic ones, but are often unable to be dated radiometrically making it difficult to know their exact ages.[11] Paleontologist Louis Jacobs, who spent time doing field work in Malawi,[citation needed] says that African beds are "in need of more field work" and will prove to be a "fertile ground ... for discovery."[11]
 Africa is considered by most paleoanthropologists to be the oldest inhabited territory on Earth, with the human species originating from the continent.[12][13] During the middle of the 20th century, anthropologists discovered many fossils and evidence of human occupation perhaps as early as 7 million years ago. Fossil remains of several species of early apelike humans thought to have evolved into modern man, such as Australopithecus afarensis (radiometrically dated to approximately 3.9–3.0 million years BC),[14] Paranthropus boisei (c. 2.3–1.4 million years BC)[15] and Homo ergaster (c. 1.9 million–600,000 years BC) have been discovered.[2]
Africa is considered by most paleoanthropologists to be the oldest inhabited territory on Earth, with the human species originating from the continent.[12][13] During the middle of the 20th century, anthropologists discovered many fossils and evidence of human occupation perhaps as early as 7 million years ago. Fossil remains of several species of early apelike humans thought to have evolved into modern man, such as Australopithecus afarensis (radiometrically dated to approximately 3.9–3.0 million years BC),[14] Paranthropus boisei (c. 2.3–1.4 million years BC)[15] and Homo ergaster (c. 1.9 million–600,000 years BC) have been discovered.[2]
Throughout humanity's prehistory, Africa (like all other continents) had no nation states, and was instead inhabited by groups of hunter-gatherers such as the Khoi and San.[16][17][18]
At the end of the Ice Ages, estimated to have been around 10,500 BC, the Sahara had again become a green fertile valley, and its African populations returned from the interior and coastal highlands in Sub-Saharan Africa[citation needed]. However, the warming and drying climate meant that by 5000 BC the Sahara region was becoming increasingly dry and hostile. The population trekked out of the Sahara region towards the Nile Valley below the Second Cataract where they made permanent or semi-permanent settlements. A major climatic recession occurred, lessening the heavy and persistent rains in Central and Eastern Africa. Since this time dry conditions have prevailed in Eastern Africa, and increasingly during the last 200 years, in Ethiopia.
The domestication of cattle in Africa preceded agriculture and seems to have existed alongside hunter-gathering cultures. It is speculated that by 6000 BC cattle were already domesticated in North Africa.[19] In the Sahara-Nile complex, people domesticated many animals including the donkey, and a small screw-horned goat which was common from Algeria to Nubia. In the year 4000 BC the climate of the Sahara started to become drier at an exceedingly fast pace.[20] This climate change caused lakes and rivers to shrink significantly and caused increasing desertification. This, in turn, decreased the amount of land conducive to settlements and helped to cause migrations of farming communities to the more tropical climate of West Africa.[20]
By the first millennium BC ironworking had been introduced in Northern Africa and quickly spread across the Sahara into the northern parts of sub-Saharan Africa[21] and by 500 BC metalworking began to become commonplace in West Africa. Ironworking was fully established by roughly 500 BC in many areas of East and West Africa, although other regions didn't begin ironworking until the early centuries AD. Copper objects from Egypt, North Africa, Nubia and Ethiopia dating from around 500 BC have been excavated in West Africa, suggesting that trans-saharan trade networks had been established by this date.[20]
An independent centre of civilisation with trading links to Phoenicia was established by Phoenicians from Tyre on the north-west African coast at Carthage.[26][27][28]
European exploration of Africa began with Ancient Greeks and Romans. In 332 BC, Alexander the Great was welcomed as a liberator in Persian-occupied Egypt. He founded Alexandria in Egypt, which would become the prosperous capital of the Ptolemaic dynasty after his death.[29] Following the conquest of North Africa's Mediterranean coastline by the Roman Empire, the area was integrated economically and culturally into the Roman system. Roman settlement occurred in modern Tunisia and elsewhere along the coast. Christianity spread across these areas from Palestine via Egypt, also passing south, beyond the borders of the Roman world into Nubia and by at least the 6th century into Ethiopia.
In the early 7th century, the newly formed Arabian Islamic Caliphate expanded into Egypt, and then into North Africa. In a short while the local Berber elite had been integrated into Muslim Arab tribes. When the Ummayad capital Damascus fell in the 8th century, the Islamic center of the Mediterranean shifted from Syria to Qayrawan in North Africa. Islamic North Africa had become diverse, and a hub for mystics, scholars, jurists and philosophers. During the above mentioned period, Islam spread to sub-Saharan Africa, mainly through trade routes and migration.[30]
By the 9th century a string of dynastic states, including the earliest Hausa states, stretched across the sub-saharan savannah from the western regions to central Sudan. The most powerful of these states were Ghana, Gao, and the Kanem-Bornu Empire. Ghana declined in the 11th century but was succeeded by the Mali Empire which consolidated much of western Sudan in the 13th century. Kanem accepted Islam in the 11th century.
In the forested regions of the West African coast, independent kingdoms grew up with little influence from the Muslim north. The Kingdom of Nri of the Igbo was established around the 9th century and was one of the first. It is also one of the oldest Kingdom in modern day Nigeria and was ruled by the Eze Nri. The Nri kingdom is famous for its elaborate bronzes, found at the town of Igbo Ukwu. The bronzes have been dated from as far back as the 9th century.[33]
The Ife, historically the first of these Yoruba city-states or kingdoms, established government under a priestly oba (ruler), (oba means 'king' or 'ruler' in the Yoruba language), called the Ooni of Ife. Ife was noted as a major religious and cultural centre in Africa, and for its unique naturalistic tradition of bronze sculpture. The Ife model of government was adapted at Oyo, where its obas or kings, called the Alaafins of Oyo once controlled a large number of other Yoruba and non Yoruba city states and Kingdoms, the Fon Kingdom of Dahomey was one of the non Yoruba domains under Oyo control.
The Almoravids were a Berber dynasty from the Sahara that spread over a wide area of northwestern Africa and the Iberian peninsula during the 11th century.[34] The Banu Hilal and Banu Ma'qil were a collection of Arab Bedouin tribes from the Arabian peninsula who migrated westwards via Egypt between the 11th and 13th centuries. Their migration resulted in the fusion of the Arabs and Berbers, where the locals were Arabized,[35] and Arab culture absorbed elements of the local culture, under the unifying framework of Islam.[36]
 Following the breakup of Mali a local leader named Sonni Ali (1464–1492) founded the Songhai Empire in the region of middle Niger and the western Sudan and took control of the trans-Saharan trade. Sonni Ali seized Timbuktu in 1468 and Jenne in 1473, building his regime on trade revenues and the cooperation of Muslim merchants. His successor Askia Mohammad I (1493–1528) made Islam the official religion, built mosques, and brought Muslim scholars, including al-Maghili (d.1504), the founder of an important tradition of Sudanic African Muslim scholarship, to Gao.[37] By the 11th century some Hausa states – such as Kano, jigawa, Katsina, and Gobir – had developed into walled towns engaging in trade, servicing caravans, and the manufacture of goods. Until the 15th century these small states were on the periphery of the major Sudanic empires of the era, paying tribute to Songhai to the west and Kanem-Borno to the east.
Following the breakup of Mali a local leader named Sonni Ali (1464–1492) founded the Songhai Empire in the region of middle Niger and the western Sudan and took control of the trans-Saharan trade. Sonni Ali seized Timbuktu in 1468 and Jenne in 1473, building his regime on trade revenues and the cooperation of Muslim merchants. His successor Askia Mohammad I (1493–1528) made Islam the official religion, built mosques, and brought Muslim scholars, including al-Maghili (d.1504), the founder of an important tradition of Sudanic African Muslim scholarship, to Gao.[37] By the 11th century some Hausa states – such as Kano, jigawa, Katsina, and Gobir – had developed into walled towns engaging in trade, servicing caravans, and the manufacture of goods. Until the 15th century these small states were on the periphery of the major Sudanic empires of the era, paying tribute to Songhai to the west and Kanem-Borno to the east.
In West Africa, the decline of the Atlantic slave trade in the 1820s caused dramatic economic shifts in local polities. The gradual decline of slave-trading, prompted by a lack of demand for slaves in the New World, increasing anti-slavery legislation in Europe and America, and the British Royal Navy's increasing presence off the West African coast, obliged African states to adopt new economies. Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard.[43]
Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers.[44] The largest powers of West Africa (the Asante Confederacy, the Kingdom of Dahomey, and the Oyo Empire) adopted different ways of adapting to the shift. Asante and Dahomey concentrated on the development of "legitimate commerce" in the form of palm oil, cocoa, timber and gold, forming the bedrock of West Africa's modern export trade. The Oyo Empire, unable to adapt, collapsed into civil wars.[45]
In the late 19th century, the European imperial powers engaged in a major territorial scramble and occupied most of the continent, creating many colonial territories, and leaving only two fully independent states: Ethiopia (known to Europeans as "Abyssinia"), and Liberia. Egypt and Sudan were never formally incorporated into any European colonial empire; however, after the British occupation of 1882, Egypt was effectively under British administration until 1922.
Portugal's overseas presence in Sub-Saharan Africa (most notably in Angola, Cape Verde, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe) lasted from the 16th century to 1975, after the Estado Novo regime was overthrown in a military coup in Lisbon. Rhodesia unilaterally declared independence from the United Kingdom in 1965, under the white minority government of Ian Smith, but was not internationally recognised as an independent state (as Zimbabwe) until 1980, when black nationalists gained power after a bitter guerrilla war. Although South Africa was one of the first African countries to gain independence, the state remained under the control of the country's white minority through a system of racial segregation known as apartheid until 1994.
Great instability was mainly the result of marginalization of ethnic groups, and graft under these leaders. For political gain, many leaders fanned ethnic conflicts that had been exacerbated, or even created, by colonial rule. In many countries, the military was perceived as being the only group that could effectively maintain order, and it ruled many nations in Africa during the 1970s and early 1980s. During the period from the early 1960s to the late 1980s, Africa had more than 70 coups and 13 presidential assassinations. Border and territorial disputes were also common, with the European-imposed borders of many nations being widely contested through armed conflicts.
Cold War conflicts between the United States and the Soviet Union, as well as the policies of the International Monetary Fund, also played a role in instability. When a country became independent for the first time, it was often expected to align with one of the two superpowers. Many countries in Northern Africa received Soviet military aid, while many in Central and Southern Africa were supported by the United States, France or both. The 1970s saw an escalation, as newly independent Angola and Mozambique aligned themselves with the Soviet Union, and the West and South Africa sought to contain Soviet influence by funding insurgency movements. There was a major famine in Ethiopia, when hundreds of thousands of people starved. Some claimed that Marxist/Soviet policies made the situation worse.[48][49][50] The most devastating military conflict in modern independent Africa has been the Second Congo War. By 2008, this conflict and its aftermath had killed 5.4 million people. Since 2003 there has been an ongoing conflict in Darfur which has become a humanitarian disaster. AIDS has also been a prevalent issue in post-colonial Africa.
In the 21th century, however, the number of armed conflicts in Africa has steadily declined. For instance, the civil war in Angola came to an end in 2002 after nearly 30 years. This has coincided with many countries abandoning communist style command economies and opening up for market reforms. The improved stability and economic reforms have lead to a great increase in forreign investment into many African nations, mainly from China, which has spurred quick economic growth in many countries, seemingly finally ending decades of stagnation and decline. Several African economomies are among the world's fasted growing as of 2011.
 From the most northerly point, Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia (37°21' N), to the most southerly point, Cape Agulhas in South Africa (34°51'15" S), is a distance of approximately 8,000 km (5,000 mi);[53] from Cape Verde, 17°33'22" W, the westernmost point, to Ras Hafun in Somalia, 51°27'52" E, the most easterly projection, is a distance of approximately 7,400 km (4,600 mi).[54] The coastline is 26,000 km (16,000 mi) long, and the absence of deep indentations of the shore is illustrated by the fact that Europe, which covers only 10,400,000 km2 (4,000,000 sq mi) – about a third of the surface of Africa – has a coastline of 32,000 km (20,000 mi).[54]
From the most northerly point, Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia (37°21' N), to the most southerly point, Cape Agulhas in South Africa (34°51'15" S), is a distance of approximately 8,000 km (5,000 mi);[53] from Cape Verde, 17°33'22" W, the westernmost point, to Ras Hafun in Somalia, 51°27'52" E, the most easterly projection, is a distance of approximately 7,400 km (4,600 mi).[54] The coastline is 26,000 km (16,000 mi) long, and the absence of deep indentations of the shore is illustrated by the fact that Europe, which covers only 10,400,000 km2 (4,000,000 sq mi) – about a third of the surface of Africa – has a coastline of 32,000 km (20,000 mi).[54]
Africa's largest country is Algeria, and its smallest country is the Seychelles, an archipelago off the east coast.[55] The smallest nation on the continental mainland is The Gambia.
According to the ancient Romans, Africa lay to the west of Egypt, while "Asia" was used to refer to Anatolia and lands to the east. A definite line was drawn between the two continents by the geographer Ptolemy (85–165 AD), indicating Alexandria along the Prime Meridian and making the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea the boundary between Asia and Africa. As Europeans came to understand the real extent of the continent, the idea of Africa expanded with their knowledge.
Geologically, Africa includes the Arabian Peninsula; the Zagros Mountains of Iran and the Anatolian Plateau of Turkey mark where the African Plate collided with Eurasia. The Afrotropic ecozone and the Saharo-Arabian desert to its north unite the region biogeographically, and the Afro-Asiatic language family unites the north linguistically.

The African Union, not to be confused with the AU Commission, is formed by the Constitutive Act of the African Union, which aims to transform the African Economic Community, a federated commonwealth, into a state under established international conventions. The African Union has a parliamentary government, known as the African Union Government, consisting of legislative, judicial and executive organs. It is led by the African Union President and Head of State, who is also the President of the Pan African Parliament. A person becomes AU President by being elected to the PAP, and subsequently gaining majority support in the PAP. The powers and authority of the President of the African Parliament derive from the Constitutive Act and the Protocol of the Pan African Parliament, as well as the inheritance of presidential authority stipulated by African treaties and by international treaties, including those subordinating the Secretary General of the OAU Secretariat (AU Commission) to the PAP. The government of the AU consists of all-union (federal), regional, state, and municipal authorities, as well as hundreds of institutions, that together manage the day-to-day affairs of the institution.
Political associations such as the African Union offer hope for greater co-operation and peace between the continent's many countries. Extensive human rights abuses still occur in several parts of Africa, often under the oversight of the state. Most of such violations occur for political reasons, often as a side effect of civil war. Countries where major human rights violations have been reported in recent times include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Sudan, Zimbabwe, and Côte d'Ivoire.

Poverty, illiteracy, malnutrition and inadequate water supply and sanitation, as well as poor health, affect a large proportion of the people who reside in the African continent. In August 2008, the World Bank[65] announced revised global poverty estimates based on a new international poverty line of $1.25 per day (versus the previous measure of $1.00). 80.5% of the Sub-Saharan Africa population was living on less than $2.50 (PPP) a day in 2005, compared with 85.7% for India.[66]
The new figures confirm that sub-Saharan Africa has been the least successful region of the world in reducing poverty ($1.25 per day); some 50% of the population living in poverty in 1981 (200 million people), a figure that rose to 58% in 1996 before dropping to 50% in 2005 (380 million people). The average poor person in sub-Saharan Africa is estimated to live on only 70 cents per day, and was poorer in 2003 than he or she was in 1973 [67] indicating increasing poverty in some areas. Some of it is attributed to unsuccessful economic liberalization programs spearheaded by foreign companies and governments, but other studies and reports have cited bad domestic government policies more than external factors.[68][69][70]
From 1995 to 2005, Africa's rate of economic growth increased, averaging 5% in 2005. Some countries experienced still higher growth rates, notably Angola, Sudan and Equatorial Guinea, all three of which had recently begun extracting their petroleum reserves or had expanded their oil extraction capacity. The continent is believed to hold 90% of the world’s cobalt, 90% of its platinum, 50% of its gold, 98% of its chromium, 70% of its tantalite,[71] 64% of its manganese and one-third of its uranium.[72] The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has 70% of the world’s coltan, and most mobile phones in the world are made with elements refined from this mineral. The DRC also has more than 30% of the world’s diamond reserves.[73] Guinea is the world’s largest exporter of bauxite.[74] As the growth in Africa has been driven mainly by services and not manufacturing or agriculture, it has been growth without jobs and without reduction in poverty levels. In fact, the food security crisis of 2008 which took place on the heels of the global financial crisis has pushed back 100 million people into food insecurity.[75]
In recent years, the People's Republic of China has built increasingly stronger ties with African nations. In 2007, Chinese companies invested a total of US$1 billion in Africa.[76]
A Harvard University study showed that Africa could easily feed itself, if only it had decent governance.[77]
 Africa's population has rapidly increased over the last 40 years, and consequently, it is relatively young. In some African states, half or more of the population is under 25 years of age.[78] The total number of people in Africa grew from 221 million in 1950 to 1 billion in 2009.[79][80]
Africa's population has rapidly increased over the last 40 years, and consequently, it is relatively young. In some African states, half or more of the population is under 25 years of age.[78] The total number of people in Africa grew from 221 million in 1950 to 1 billion in 2009.[79][80]
Speakers of Bantu languages (part of the Niger–Congo family) are the majority in southern, central and southeast Africa. The Bantu-speaking farmers from West Africa's inland savanna progressively expanded over most of Sub-Saharan Africa.[81] But there are also several Nilotic groups in South Sudan and East Africa, the mixed Swahili people on the Swahili Coast, and a few remaining indigenous Khoisan ('San' or 'Bushmen') and Pygmy peoples in southern and central Africa, respectively. Bantu-speaking Africans also predominate in Gabon and Equatorial Guinea, and are found in parts of southern Cameroon. In the Kalahari Desert of Southern Africa, the distinct people known as the Bushmen (also "San", closely related to, but distinct from "Hottentots") have long been present. The San are physically distinct from other Africans and are the indigenous people of southern Africa. Pygmies are the pre-Bantu indigenous peoples of central Africa.[82]
The peoples of North Africa comprise two main groups: Berbers and Arabic-speaking peoples in the west, and Egyptians and Libyans in the east. The Arabs who arrived in the 7th century introduced the Arabic language and Islam to North Africa. The Semitic Phoenicians (who founded Carthage) and Hyksos, the Indo-Iranian Alans, the Indo- European Greeks, Romans and Vandals settled in North Africa as well. Berbers still make up the majority in Morocco, while they are a significant minority within Algeria. They are also present in Tunisia and Libya.[83] The Berber-speaking Tuareg and other often-nomadic peoples are the principal inhabitants of the Saharan interior of North Africa.
Some Ethiopian and Eritrean groups (like the Amhara and Tigrayans, collectively known as Habesha) speak languages from the Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, while the Oromo and Somali speak languages from the Cushitic branch of Afro-Asiatic. Sudan is mostly inhabited by Nubian and Beja people, with northern Mauritania somewhat similarly structured.
Prior to the decolonization movements of the post-World War II era, Europeans were represented in every part of Africa.[84] Decolonisation during the 1960s and 1970s often resulted in the mass emigration of European-descended settlers out of Africa – especially from Algeria and Morocco (1.6 million pieds-noirs in North Africa),[85] Kenya, Congo,[86] Rhodesia, Mozambique and Angola.[87] By the end of 1977, more than one million Portuguese were thought to have returned from Africa.[88] Nevertheless, White Africans remain an important minority in many African states, particularly South Africa, Zimbabwe, Namibia and Réunion.[89] The African country with the largest White African population is South Africa.[90] The Afrikaners, the Anglo-Africans (of British origin) and the Coloureds are the largest European-descended groups in Africa today.
European colonization also brought sizable groups of Asians, particularly people from the Indian subcontinent, to British colonies. Large Indian communities are found in South Africa, and smaller ones are present in Kenya, Tanzania, and some other southern and East African countries. The large Indian community in Uganda was expelled by the dictator Idi Amin in 1972, though many have since returned. The islands in the Indian Ocean are also populated primarily by people of Asian origin, often mixed with Africans and Europeans. The Malagasy people of Madagascar are an Austronesian people, but those along the coast are generally mixed with Bantu, Arab, Indian and European origins. Malay and Indian ancestries are also important components in the group of people known in South Africa as Cape Coloureds (people with origins in two or more races and continents). During the 20th century, small but economically important communities of Lebanese and Chinese[76] have also developed in the larger coastal cities of West and East Africa, respectively.[91]

Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa and Zimbabwe have Test status, while Kenya is the leading non-test team in One-Day International cricket and has attained permanent One-Day International status. The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup. Morocco in northern Africa has also hosted the 2002 Morocco Cup, but the national team has never qualified for a major tournament. Rugby is a popular sport in South Africa and Namibia.

The continent is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, both the Suez Canal and the Red Sea along the Sinai Peninsula to the northeast, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The continent includes Madagascar and various archipelagoes and has 54 sovereign states ("countries") and two states with limited recognition.
Africa, particularly central Eastern Africa, is widely regarded within the scientific community to be the origin of humans and the Hominidae clade (great apes), as evidenced by the discovery of the earliest hominids and their ancestors, as well as later ones that have been dated to around seven million years ago – including Sahelanthropus tchadensis, Australopithecus africanus, A. afarensis, Homo erectus, H. habilis and H. ergaster – with the earliest Homo sapiens (modern human) found in Ethiopia being dated to circa 200,000 years ago.[3]
Africa straddles the equator and encompasses numerous climate areas; it is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate to southern temperate zones.[4] The African expected economic growth rate is at about 5.0% for 2010 and 5.5% in 2011.[5]
Afri was a Latin name used to refer to the Carthaginians who dwelt in North Africa in modern-day Tunisia. Their name is usually connected with Phoenician afar, "dust", but a 1981 hypothesis[6] has asserted that it stems from the Berber word ifri or ifran meaning "cave" and "caves", in reference to cave dwellers.[7] Africa or Ifri or Afer[7] is the name of Banu Ifran from Algeria and Tripolitania (Berber Tribe of Yafran).[8]
Under Roman rule, Carthage became the capital of Africa Province, which also included the coastal part of modern Libya.[9] The Latin suffix "-ica" can sometimes be used to denote a land (e.g., in Celtica from Celtes, as used by Julius Caesar). The later Muslim kingdom of Ifriqiya, modern-day Tunisia, also preserved a form of the name.
Other etymological hypotheses that have been postulated for the ancient name "Africa":
- the 1st century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus (Ant. 1.15) asserted that it was named for Epher, grandson of Abraham according to Gen. 25:4, whose descendants, he claimed, had invaded Libya.
- Latin word aprica ("sunny") mentioned by Isidore of Seville in Etymologiae XIV.5.2.
- the Greek word aphrike (Αφρική), meaning "without cold." This was proposed by historian Leo Africanus (1488–1554), who suggested the Greek word phrike (φρίκη, meaning "cold and horror"), combined with the privative prefix "a-", thus indicating a land free of cold and horror.
- Massey, in 1881, derived an etymology from the Egyptian af-rui-ka, "to turn toward the opening of the Ka." The Ka is the energetic double of every person and "opening of the Ka" refers to a womb or birthplace. Africa would be, for the Egyptians, "the birthplace."[10]
- yet another hypothesis was proposed by Michèle Fruyt in Revue de Philologie 50, 1976: 221–238, linking the Latin word with africus 'south wind', which would be of Umbrian origin and mean originally 'rainy wind'.
History
Main article: History of Africa
Further information: History of North Africa, History of West Africa, History of Central Africa, History of East Africa, and History of Southern Africa
Paleohistory

The African prosauropod Massospondylus.
Early Jurassic strata are distributed in a similar fashion to Late Triassic beds, with more common outcrops in the south and less common fossil beds which are predominated by tracks to the north.[11] As the Jurassic proceeded, larger and more iconic groups of dinosaurs like sauropods and ornithopods proliferated in Africa.[11] Middle Jurassic strata are neither well represented nor well studied in Africa.[11] Late Jurassic strata are also poorly represented apart from the spectacular Tendaguru fauna in Tanzania.[11] The Late Jurassic life of Tendaguru is very similar to that found in western North America's Morrison Formation.[11]
Midway through the Mesozoic, about 150–160 million years ago, Madagascar separated from Africa, although it remained connected to India and the rest of the Gondwanan landmasses.[11] Fossils from Madagascar include abelisaurs and titanosaurs.[11]

The African theropod Spinosaurus was the largest known carnivorous dinosaur.
By contrast to Madagascar, mainland Africa was relatively stable in position through-out the Mesozoic.[11] Despite the stable position, major changes occurred to its relation to other landmasses as the remains of Pangea continued to break apart.[11] By the beginning of the Late Cretaceous epoch South America had split off from Africa, completing the southern half of the Atlantic Ocean.[11] This event had a profound effect on global climate by altering ocean currents.[11]
During the Cretaceous, Africa was populated by allosauroids and spinosaurids, including the largest known carnivorous dinosaurs.[11] Titanosaurs were significant herbivores in its ancient ecosystems.[11] Cretaceous sites are more common than Jurassic ones, but are often unable to be dated radiometrically making it difficult to know their exact ages.[11] Paleontologist Louis Jacobs, who spent time doing field work in Malawi,[citation needed] says that African beds are "in need of more field work" and will prove to be a "fertile ground ... for discovery."[11]
Prehistory

Lucy, an Australopithecus afarensis skeleton discovered on November 24, 1974, in the Awash Valley of Ethiopia's Afar Depression
Throughout humanity's prehistory, Africa (like all other continents) had no nation states, and was instead inhabited by groups of hunter-gatherers such as the Khoi and San.[16][17][18]
At the end of the Ice Ages, estimated to have been around 10,500 BC, the Sahara had again become a green fertile valley, and its African populations returned from the interior and coastal highlands in Sub-Saharan Africa[citation needed]. However, the warming and drying climate meant that by 5000 BC the Sahara region was becoming increasingly dry and hostile. The population trekked out of the Sahara region towards the Nile Valley below the Second Cataract where they made permanent or semi-permanent settlements. A major climatic recession occurred, lessening the heavy and persistent rains in Central and Eastern Africa. Since this time dry conditions have prevailed in Eastern Africa, and increasingly during the last 200 years, in Ethiopia.
The domestication of cattle in Africa preceded agriculture and seems to have existed alongside hunter-gathering cultures. It is speculated that by 6000 BC cattle were already domesticated in North Africa.[19] In the Sahara-Nile complex, people domesticated many animals including the donkey, and a small screw-horned goat which was common from Algeria to Nubia. In the year 4000 BC the climate of the Sahara started to become drier at an exceedingly fast pace.[20] This climate change caused lakes and rivers to shrink significantly and caused increasing desertification. This, in turn, decreased the amount of land conducive to settlements and helped to cause migrations of farming communities to the more tropical climate of West Africa.[20]
By the first millennium BC ironworking had been introduced in Northern Africa and quickly spread across the Sahara into the northern parts of sub-Saharan Africa[21] and by 500 BC metalworking began to become commonplace in West Africa. Ironworking was fully established by roughly 500 BC in many areas of East and West Africa, although other regions didn't begin ironworking until the early centuries AD. Copper objects from Egypt, North Africa, Nubia and Ethiopia dating from around 500 BC have been excavated in West Africa, suggesting that trans-saharan trade networks had been established by this date.[20]
Early civilizations
Main article: Ancient African history
At about 3300 BC, the historical record opens in Northern Africa with the rise of literacy in the Pharaonic civilisation of Ancient Egypt.[22] One of the world's earliest and longest-lasting civilizations, the Egyptian state continued, with varying levels of influence over other areas, until 343 BC.[23][24] Egyptian influence reached deep into modern-day Libya, north to Crete[25] and Canaan[citation needed], and south to the kingdoms of Aksum[citation needed] and Nubia[citation needed].An independent centre of civilisation with trading links to Phoenicia was established by Phoenicians from Tyre on the north-west African coast at Carthage.[26][27][28]
European exploration of Africa began with Ancient Greeks and Romans. In 332 BC, Alexander the Great was welcomed as a liberator in Persian-occupied Egypt. He founded Alexandria in Egypt, which would become the prosperous capital of the Ptolemaic dynasty after his death.[29] Following the conquest of North Africa's Mediterranean coastline by the Roman Empire, the area was integrated economically and culturally into the Roman system. Roman settlement occurred in modern Tunisia and elsewhere along the coast. Christianity spread across these areas from Palestine via Egypt, also passing south, beyond the borders of the Roman world into Nubia and by at least the 6th century into Ethiopia.
In the early 7th century, the newly formed Arabian Islamic Caliphate expanded into Egypt, and then into North Africa. In a short while the local Berber elite had been integrated into Muslim Arab tribes. When the Ummayad capital Damascus fell in the 8th century, the Islamic center of the Mediterranean shifted from Syria to Qayrawan in North Africa. Islamic North Africa had become diverse, and a hub for mystics, scholars, jurists and philosophers. During the above mentioned period, Islam spread to sub-Saharan Africa, mainly through trade routes and migration.[30]
9th–18th centuries
Pre-colonial Africa possessed perhaps as many as 10,000 different states and polities[32] characterised by many different sorts of political organisation and rule. These included small family groups of hunter-gatherers such as the San people of southern Africa; larger, more structured groups such as the family clan groupings of the Bantu-speaking people of central and southern Africa, heavily structured clan groups in the Horn of Africa, the large Sahelian kingdoms, and autonomous city-states and kingdoms such as those of the Akan, Yoruba and Igbo people (also misspelled as Ibo) in West Africa, and the Swahili coastal trading towns of East Africa.By the 9th century a string of dynastic states, including the earliest Hausa states, stretched across the sub-saharan savannah from the western regions to central Sudan. The most powerful of these states were Ghana, Gao, and the Kanem-Bornu Empire. Ghana declined in the 11th century but was succeeded by the Mali Empire which consolidated much of western Sudan in the 13th century. Kanem accepted Islam in the 11th century.
In the forested regions of the West African coast, independent kingdoms grew up with little influence from the Muslim north. The Kingdom of Nri of the Igbo was established around the 9th century and was one of the first. It is also one of the oldest Kingdom in modern day Nigeria and was ruled by the Eze Nri. The Nri kingdom is famous for its elaborate bronzes, found at the town of Igbo Ukwu. The bronzes have been dated from as far back as the 9th century.[33]
The Ife, historically the first of these Yoruba city-states or kingdoms, established government under a priestly oba (ruler), (oba means 'king' or 'ruler' in the Yoruba language), called the Ooni of Ife. Ife was noted as a major religious and cultural centre in Africa, and for its unique naturalistic tradition of bronze sculpture. The Ife model of government was adapted at Oyo, where its obas or kings, called the Alaafins of Oyo once controlled a large number of other Yoruba and non Yoruba city states and Kingdoms, the Fon Kingdom of Dahomey was one of the non Yoruba domains under Oyo control.
The Almoravids were a Berber dynasty from the Sahara that spread over a wide area of northwestern Africa and the Iberian peninsula during the 11th century.[34] The Banu Hilal and Banu Ma'qil were a collection of Arab Bedouin tribes from the Arabian peninsula who migrated westwards via Egypt between the 11th and 13th centuries. Their migration resulted in the fusion of the Arabs and Berbers, where the locals were Arabized,[35] and Arab culture absorbed elements of the local culture, under the unifying framework of Islam.[36]

Ruins of Great Zimbabwe (11th–15th c.)
Height of slave trade
See also: Arab slave trade and Atlantic slave trade
Slavery had long been practiced in Africa.[38][39] Between the 7th and 20th centuries, Arab slave trade (also known as slavery in the East) took 18 million slaves from Africa via trans-Saharan and Indian Ocean routes. Between the 15th and the 19th centuries (500 years), the Atlantic slave trade took an estimated 7–12 million slaves to the New World.[40][41][42]In West Africa, the decline of the Atlantic slave trade in the 1820s caused dramatic economic shifts in local polities. The gradual decline of slave-trading, prompted by a lack of demand for slaves in the New World, increasing anti-slavery legislation in Europe and America, and the British Royal Navy's increasing presence off the West African coast, obliged African states to adopt new economies. Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard.[43]
Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers.[44] The largest powers of West Africa (the Asante Confederacy, the Kingdom of Dahomey, and the Oyo Empire) adopted different ways of adapting to the shift. Asante and Dahomey concentrated on the development of "legitimate commerce" in the form of palm oil, cocoa, timber and gold, forming the bedrock of West Africa's modern export trade. The Oyo Empire, unable to adapt, collapsed into civil wars.[45]
Colonialism and the "Scramble for Africa"
Main article: Colonization of Africa
Further information: Scramble for Africa
In the late 19th century, the European imperial powers engaged in a major territorial scramble and occupied most of the continent, creating many colonial territories, and leaving only two fully independent states: Ethiopia (known to Europeans as "Abyssinia"), and Liberia. Egypt and Sudan were never formally incorporated into any European colonial empire; however, after the British occupation of 1882, Egypt was effectively under British administration until 1922.
Berlin Conference
The Berlin Conference held in 1884–85 was an important event in the political future of African ethnic groups. It was convened by King Leopold II of Belgium, and attended by the European powers that laid claim to African territories. It sought to bring an end to the Scramble for Africa by European powers by agreeing on political division and spheres of influence. They set up the political divisions of the continent, by spheres of interest, that exist in Africa today.Independence struggles
Imperial rule by Europeans would continue until after the conclusion of World War II, when almost all remaining colonial territories gradually obtained formal independence. Independence movements in Africa gained momentum following World War II, which left the major European powers weakened. In 1951, Libya, a former Italian colony, gained independence. In 1956, Tunisia and Morocco won their independence from France.[46] Ghana followed suit the next year (March 1957),[47] becoming the first of the sub-Saharan colonies to be freed. Most of the rest of the continent became independent over the next decade.Portugal's overseas presence in Sub-Saharan Africa (most notably in Angola, Cape Verde, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe) lasted from the 16th century to 1975, after the Estado Novo regime was overthrown in a military coup in Lisbon. Rhodesia unilaterally declared independence from the United Kingdom in 1965, under the white minority government of Ian Smith, but was not internationally recognised as an independent state (as Zimbabwe) until 1980, when black nationalists gained power after a bitter guerrilla war. Although South Africa was one of the first African countries to gain independence, the state remained under the control of the country's white minority through a system of racial segregation known as apartheid until 1994.
Post-colonial Africa
Today, Africa contains 54 sovereign countries, most of which still have the borders drawn during the era of European colonialism. Since colonialism, African states have frequently been hampered by instability, corruption, violence, and authoritarianism. The vast majority of African states are republics that operate under some form of the presidential system of rule. However, few of them have been able to sustain democratic governments on a permanent basis, and many have instead cycled through a series of coups, producing military dictatorships.Great instability was mainly the result of marginalization of ethnic groups, and graft under these leaders. For political gain, many leaders fanned ethnic conflicts that had been exacerbated, or even created, by colonial rule. In many countries, the military was perceived as being the only group that could effectively maintain order, and it ruled many nations in Africa during the 1970s and early 1980s. During the period from the early 1960s to the late 1980s, Africa had more than 70 coups and 13 presidential assassinations. Border and territorial disputes were also common, with the European-imposed borders of many nations being widely contested through armed conflicts.
Cold War conflicts between the United States and the Soviet Union, as well as the policies of the International Monetary Fund, also played a role in instability. When a country became independent for the first time, it was often expected to align with one of the two superpowers. Many countries in Northern Africa received Soviet military aid, while many in Central and Southern Africa were supported by the United States, France or both. The 1970s saw an escalation, as newly independent Angola and Mozambique aligned themselves with the Soviet Union, and the West and South Africa sought to contain Soviet influence by funding insurgency movements. There was a major famine in Ethiopia, when hundreds of thousands of people starved. Some claimed that Marxist/Soviet policies made the situation worse.[48][49][50] The most devastating military conflict in modern independent Africa has been the Second Congo War. By 2008, this conflict and its aftermath had killed 5.4 million people. Since 2003 there has been an ongoing conflict in Darfur which has become a humanitarian disaster. AIDS has also been a prevalent issue in post-colonial Africa.
In the 21th century, however, the number of armed conflicts in Africa has steadily declined. For instance, the civil war in Angola came to an end in 2002 after nearly 30 years. This has coincided with many countries abandoning communist style command economies and opening up for market reforms. The improved stability and economic reforms have lead to a great increase in forreign investment into many African nations, mainly from China, which has spurred quick economic growth in many countries, seemingly finally ending decades of stagnation and decline. Several African economomies are among the world's fasted growing as of 2011.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Africa
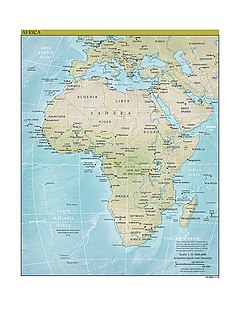
Africa is the largest of the three great southward projections from the largest landmass of the Earth. Separated from Europe by the Mediterranean Sea, it is joined to Asia at its northeast extremity by the Isthmus of Suez (transected by the Suez Canal), 163 km (101 mi) wide.[51] (Geopolitically, Egypt's Sinai Peninsula east of the Suez Canal is often considered part of Africa, as well.)[52]
Biomes of Africa.
Africa's largest country is Algeria, and its smallest country is the Seychelles, an archipelago off the east coast.[55] The smallest nation on the continental mainland is The Gambia.
According to the ancient Romans, Africa lay to the west of Egypt, while "Asia" was used to refer to Anatolia and lands to the east. A definite line was drawn between the two continents by the geographer Ptolemy (85–165 AD), indicating Alexandria along the Prime Meridian and making the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea the boundary between Asia and Africa. As Europeans came to understand the real extent of the continent, the idea of Africa expanded with their knowledge.
Geologically, Africa includes the Arabian Peninsula; the Zagros Mountains of Iran and the Anatolian Plateau of Turkey mark where the African Plate collided with Eurasia. The Afrotropic ecozone and the Saharo-Arabian desert to its north unite the region biogeographically, and the Afro-Asiatic language family unites the north linguistically.
Climate

A map of Africa showing the ecological break around the Sahara desert
Main article: Climate of Africa
The climate of Africa ranges from tropical to subarctic on its highest peaks. Its northern half is primarily desert or arid, while its central and southern areas contain both savanna plains and very dense jungle (rainforest) regions. In between, there is a convergence where vegetation patterns such as sahel, and steppe dominate. Africa is the hottest continent on earth; drylands and deserts comprise 60% of the entire land surface.[56] The record for the highest temperature recorded was set in Libya in 1922 (58 °C (136 °F)).[57]Fauna
Main article: Fauna of Africa
Africa boasts perhaps the world's largest combination of density and "range of freedom" of wild animal populations and diversity, with wild populations of large carnivores (such as lions, hyenas, and cheetahs) and herbivores (such as buffalo, elephants, camels, and giraffes) ranging freely on primarily open non-private plains. It is also home to a variety of "jungle" animals including snakes and primates and aquatic life such as crocodiles and amphibians. In addition, Africa has the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna.Ecology
Deforestation is affecting Africa at twice the world rate, according to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).[58] According to the University of Pennsylvania African Studies Center, 31% of Africa's pasture lands and 19% of its forests and woodlands are classified as degraded, and Africa is losing over four million hectares of forest every year, which is twice the average deforestation rate compared to the rest of the world.[56] Some sources claim that deforestation has already destroyed roughly 90% of the original, virgin forests in West Africa.[59] Since the arrival of humans 2000 years ago, Madagascar has lost more than 90% of its original forest.[60] About 65% of Africa's agricultural land suffers from soil degradation.[61]Biodiversity
Africa has over 3,000 protected areas, with 198 marine protected areas, 50 biosphere reserves and 80 wetlands reserves. Significant habitat destruction, increases in human population and poaching are reducing Africa's biological diversity. Human encroachment, civil unrest and the introduction of non-native species threatens biodiversity in Africa. This has been exacerbated by administrative problems, inadequate personnel and funding problems.[56]Politics
There are clear signs of increased networking among African organisations and states. For example, in the civil war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (former Zaire), rather than rich, non-African countries intervening, neighbouring African countries became involved (see also Second Congo War). Since the conflict began in 1998, the estimated death toll has reached 5 million.The African Union
Main article: African Union
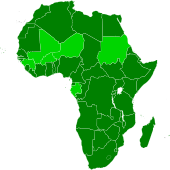
The African Union (AU) is a 54 member federation consisting of all of Africa's states except Morocco. The union was formed, with Addis Ababa, Ethiopia as its headquarters, on 26 June 2001. The union was officially established on 9 July 2002[62] as a successor to the Organisation of African Unity (OAU). In July 2004, the African Union's Pan-African Parliament (PAP) was relocated to Midrand, in South Africa, but the African Commission on Human and Peoples' Rights remained in Addis Ababa. There is a policy in effect to decentralize the African Federation's institutions so that they are shared by all the states.The African Union, not to be confused with the AU Commission, is formed by the Constitutive Act of the African Union, which aims to transform the African Economic Community, a federated commonwealth, into a state under established international conventions. The African Union has a parliamentary government, known as the African Union Government, consisting of legislative, judicial and executive organs. It is led by the African Union President and Head of State, who is also the President of the Pan African Parliament. A person becomes AU President by being elected to the PAP, and subsequently gaining majority support in the PAP. The powers and authority of the President of the African Parliament derive from the Constitutive Act and the Protocol of the Pan African Parliament, as well as the inheritance of presidential authority stipulated by African treaties and by international treaties, including those subordinating the Secretary General of the OAU Secretariat (AU Commission) to the PAP. The government of the AU consists of all-union (federal), regional, state, and municipal authorities, as well as hundreds of institutions, that together manage the day-to-day affairs of the institution.
Political associations such as the African Union offer hope for greater co-operation and peace between the continent's many countries. Extensive human rights abuses still occur in several parts of Africa, often under the oversight of the state. Most of such violations occur for political reasons, often as a side effect of civil war. Countries where major human rights violations have been reported in recent times include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Sudan, Zimbabwe, and Côte d'Ivoire.
 A clickable Euler diagram showing the relationships between various multinational African organisations.v • d • e | |
Economy

Map of the African Economic Community.
Main article: Economy of Africa
See also: Economy of the African Union
Although it has abundant natural resources, Africa remains the world's poorest and most underdeveloped continent, the result of a variety of causes that may include the spread of deadly diseases and viruses (notably HIV/AIDS and malaria), corrupt governments that have often committed serious human rights violations, failed central planning, high levels of illiteracy, lack of access to foreign capital, and frequent tribal and military conflict (ranging from guerrilla warfare to genocide).[63] According to the United Nations' Human Development Report in 2003, the bottom 25 ranked nations (151st to 175th) were all African.[64]Poverty, illiteracy, malnutrition and inadequate water supply and sanitation, as well as poor health, affect a large proportion of the people who reside in the African continent. In August 2008, the World Bank[65] announced revised global poverty estimates based on a new international poverty line of $1.25 per day (versus the previous measure of $1.00). 80.5% of the Sub-Saharan Africa population was living on less than $2.50 (PPP) a day in 2005, compared with 85.7% for India.[66]
The new figures confirm that sub-Saharan Africa has been the least successful region of the world in reducing poverty ($1.25 per day); some 50% of the population living in poverty in 1981 (200 million people), a figure that rose to 58% in 1996 before dropping to 50% in 2005 (380 million people). The average poor person in sub-Saharan Africa is estimated to live on only 70 cents per day, and was poorer in 2003 than he or she was in 1973 [67] indicating increasing poverty in some areas. Some of it is attributed to unsuccessful economic liberalization programs spearheaded by foreign companies and governments, but other studies and reports have cited bad domestic government policies more than external factors.[68][69][70]
From 1995 to 2005, Africa's rate of economic growth increased, averaging 5% in 2005. Some countries experienced still higher growth rates, notably Angola, Sudan and Equatorial Guinea, all three of which had recently begun extracting their petroleum reserves or had expanded their oil extraction capacity. The continent is believed to hold 90% of the world’s cobalt, 90% of its platinum, 50% of its gold, 98% of its chromium, 70% of its tantalite,[71] 64% of its manganese and one-third of its uranium.[72] The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has 70% of the world’s coltan, and most mobile phones in the world are made with elements refined from this mineral. The DRC also has more than 30% of the world’s diamond reserves.[73] Guinea is the world’s largest exporter of bauxite.[74] As the growth in Africa has been driven mainly by services and not manufacturing or agriculture, it has been growth without jobs and without reduction in poverty levels. In fact, the food security crisis of 2008 which took place on the heels of the global financial crisis has pushed back 100 million people into food insecurity.[75]
In recent years, the People's Republic of China has built increasingly stronger ties with African nations. In 2007, Chinese companies invested a total of US$1 billion in Africa.[76]
A Harvard University study showed that Africa could easily feed itself, if only it had decent governance.[77]
Demographics
Main articles: African people and Demographics of Africa

Woman from Benin
Speakers of Bantu languages (part of the Niger–Congo family) are the majority in southern, central and southeast Africa. The Bantu-speaking farmers from West Africa's inland savanna progressively expanded over most of Sub-Saharan Africa.[81] But there are also several Nilotic groups in South Sudan and East Africa, the mixed Swahili people on the Swahili Coast, and a few remaining indigenous Khoisan ('San' or 'Bushmen') and Pygmy peoples in southern and central Africa, respectively. Bantu-speaking Africans also predominate in Gabon and Equatorial Guinea, and are found in parts of southern Cameroon. In the Kalahari Desert of Southern Africa, the distinct people known as the Bushmen (also "San", closely related to, but distinct from "Hottentots") have long been present. The San are physically distinct from other Africans and are the indigenous people of southern Africa. Pygmies are the pre-Bantu indigenous peoples of central Africa.[82]
The peoples of North Africa comprise two main groups: Berbers and Arabic-speaking peoples in the west, and Egyptians and Libyans in the east. The Arabs who arrived in the 7th century introduced the Arabic language and Islam to North Africa. The Semitic Phoenicians (who founded Carthage) and Hyksos, the Indo-Iranian Alans, the Indo- European Greeks, Romans and Vandals settled in North Africa as well. Berbers still make up the majority in Morocco, while they are a significant minority within Algeria. They are also present in Tunisia and Libya.[83] The Berber-speaking Tuareg and other often-nomadic peoples are the principal inhabitants of the Saharan interior of North Africa.
Some Ethiopian and Eritrean groups (like the Amhara and Tigrayans, collectively known as Habesha) speak languages from the Semitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, while the Oromo and Somali speak languages from the Cushitic branch of Afro-Asiatic. Sudan is mostly inhabited by Nubian and Beja people, with northern Mauritania somewhat similarly structured.
Prior to the decolonization movements of the post-World War II era, Europeans were represented in every part of Africa.[84] Decolonisation during the 1960s and 1970s often resulted in the mass emigration of European-descended settlers out of Africa – especially from Algeria and Morocco (1.6 million pieds-noirs in North Africa),[85] Kenya, Congo,[86] Rhodesia, Mozambique and Angola.[87] By the end of 1977, more than one million Portuguese were thought to have returned from Africa.[88] Nevertheless, White Africans remain an important minority in many African states, particularly South Africa, Zimbabwe, Namibia and Réunion.[89] The African country with the largest White African population is South Africa.[90] The Afrikaners, the Anglo-Africans (of British origin) and the Coloureds are the largest European-descended groups in Africa today.
European colonization also brought sizable groups of Asians, particularly people from the Indian subcontinent, to British colonies. Large Indian communities are found in South Africa, and smaller ones are present in Kenya, Tanzania, and some other southern and East African countries. The large Indian community in Uganda was expelled by the dictator Idi Amin in 1972, though many have since returned. The islands in the Indian Ocean are also populated primarily by people of Asian origin, often mixed with Africans and Europeans. The Malagasy people of Madagascar are an Austronesian people, but those along the coast are generally mixed with Bantu, Arab, Indian and European origins. Malay and Indian ancestries are also important components in the group of people known in South Africa as Cape Coloureds (people with origins in two or more races and continents). During the 20th century, small but economically important communities of Lebanese and Chinese[76] have also developed in the larger coastal cities of West and East Africa, respectively.[91]
Languages
Main article: Languages of Africa
By most estimates, well over a thousand languages (UNESCO has estimated around two thousand) are spoken in Africa.[92] Most are of African origin, though some are of European or Asian origin. Africa is the most multilingual continent in the world, and it is not rare for individuals to fluently speak not only multiple African languages, but one or more European ones as well. There are four major language families indigenous to Africa.- The Afro-Asiatic languages are a language family of about 240 languages and 285 million people widespread throughout the Horn of Africa, North Africa, the Sahel, and Southwest Asia.
- The Nilo-Saharan language family consists of more than a hundred languages spoken by 30 million people. Nilo-Saharan languages are spoken by Nilotic tribes in Chad, Ethiopia, Kenya, Sudan, South Sudan, Uganda, and northern Tanzania.
- The Niger–Congo language family covers much of Sub-Saharan Africa and is probably the largest language family in the world in terms of different languages.
- The Khoisan languages number about fifty and are spoken in Southern Africa by approximately 120,000 people. Many of the Khoisan languages are endangered. The Khoi and San peoples are considered the original inhabitants of this part of Africa.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Africa
Some[which?] aspects of traditional African cultures have become less practiced in recent years as a result of years of neglect and suppression by colonial and post-colonial regimes. There is now a resurgence in the attempts to rediscover and revalourise African traditional cultures, under such movements as the African Renaissance, led by Thabo Mbeki, Afrocentrism, led by a group of scholars, including Molefi Asante, as well as the increasing recognition of traditional spiritualism through decriminalization of Vodou and other forms of spirituality. In recent years, traditional African culture has become synonymous with rural poverty and subsistence farming.Visual art and architecture
African art and architecture reflect the diversity of African cultures. The oldest existing examples of art from Africa are 82,000-year-old beads made from Nassarius shells that were found in the Aterian levels at Grotte des Pigeons, Taforalt, Morocco.[citation needed] The Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt was the world's tallest structure for 4,000 years, until the completion of Lincoln Cathedral around the year 1300. The stone ruins of Great Zimbabwe are also noteworthy for their architecture, and the complexity of monolithic churches at Lalibela, Ethiopia, of which the Church of Saint George is representative.[citation needed]
A street musician performing in South Africa
Music and dance
Main article: Music of Africa
Egypt has long been a cultural focus of the Arab world, while remembrance of the rhythms of sub-Saharan Africa, in particular West Africa, was transmitted through the Atlantic slave trade to modern samba, blues, jazz, reggae, hip hop, and rock. The 1950s through the 1970s saw a conglomeration of these various styles with the popularization of Afrobeat and Highlife music. Modern music of the continent includes the highly complex choral singing of southern Africa and the dance rhythms of the musical genre of soukous, dominated by the music of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Indigenous musical and dance traditions of Africa are maintained by oral traditions, and they are distinct from the music and dance styles of North Africa and Southern Africa. Arab influences are visible in North African music and dance and, in Southern Africa, Western influences are apparent due to colonisation.Sports
Fifty-three African countries have football (soccer) teams in the Confederation of African Football, while Cameroon, Nigeria, Senegal, and Ghana have advanced to the knockout stage of recent FIFA World Cups. South Africa hosted the 2010 World Cup tournament, becoming the first African country to do so. According to FIFA ranking, Egypt currently has the best soccer team in Africa. Their team has won the African Cup 7 times, and a record-making 3 times in a row.Cricket is popular in some African nations. South Africa and Zimbabwe have Test status, while Kenya is the leading non-test team in One-Day International cricket and has attained permanent One-Day International status. The three countries jointly hosted the 2003 Cricket World Cup. Namibia is the other African country to have played in a World Cup. Morocco in northern Africa has also hosted the 2002 Morocco Cup, but the national team has never qualified for a major tournament. Rugby is a popular sport in South Africa and Namibia.
Religion

The Great Mosque of Kairouan, erected in 670, is the oldest mosque in North Africa,[93] Kairouan, Tunisia.
Main article: Religion in Africa
Africans profess a wide variety of religious beliefs[94] and statistics on religious affiliation are difficult to come by since they are too sensitive a topic for governments with mixed populations.[95] According to the World Book Encyclopedia, Islam is the largest religion in Africa, followed by Christianity. However, according to Encyclopedia Britannica, 45% of the population are Christians, 40% are Muslims and less than 15% continue to follow traditional African religions. A small number of Africans are Hindu, Baha'i, or have beliefs from the Judaic tradition. Examples of African Jews are the Beta Israel, Lemba peoples and the Abayudaya of Eastern Uganda. There is also a small minority of Africans who are non-religious.Territories and regions
Main articles: List of regions of Africa and List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa
The countries in this table are categorised according to the scheme for geographic subregions used by the United Nations, and data included are per sources in cross-referenced articles. Where they differ, provisos are clearly indicated.| Name of region[96] and territory, with flag | Area (km²) | Population (2009 est) except where noted | Density (per km²) | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Africa | ||||
| 27,830 | 8,988,091[97] | 322.9 | Bujumbura | |
| 2,170 | 752,438[97] | 346.7 | Moroni | |
| 23,000 | 516,055[97] | 22.4 | Djibouti | |
| 121,320 | 5,647,168[97] | 46.5 | Asmara | |
| 1,127,127 | 85,237,338[97] | 75.6 | Addis Ababa | |
| 582,650 | 39,002,772[97] | 66.0 | Nairobi | |
| 587,040 | 20,653,556[97] | 35.1 | Antananarivo | |
| 118,480 | 14,268,711[97] | 120.4 | Lilongwe | |
| 2,040 | 1,284,264[97] | 629.5 | Port Louis | |
| 374 | 223,765[97] | 489.7 | Mamoudzou | |
| 801,590 | 21,669,278[97] | 27.0 | Maputo | |
| 2,512 | 743,981(2002) | 296.2 | Saint-Denis | |
| 26,338 | 10,473,282[97] | 397.6 | Kigali | |
| 455 | 87,476[97] | 192.2 | Victoria | |
| 637,657 | 9,832,017[97] | 15.4 | Mogadishu | |
| 945,087 | 41,048,532[97] | 43.3 | Dodoma | |
| 236,040 | 32,369,558[97] | 137.1 | Kampala | |
| 752,614 | 11,862,740[97] | 15.7 | Lusaka | |
| Central Africa | ||||
| 1,246,700 | 12,799,293[97] | 10.3 | Luanda | |
| 475,440 | 18,879,301[97] | 39.7 | Yaoundé | |
| 622,984 | 4,511,488[97] | 7.2 | Bangui | |
| 1,284,000 | 10,329,208[97] | 8.0 | N'Djamena | |
| 342,000 | 4,012,809[97] | 11.7 | Brazzaville | |
| 2,345,410 | 68,692,542[97] | 29.2 | Kinshasa | |
| 28,051 | 633,441[97] | 22.6 | Malabo | |
| 267,667 | 1,514,993[97] | 5.6 | Libreville | |
| 1,001 | 212,679[97] | 212.4 | São Tomé | |
| Northern Africa | ||||
| 2,381,740 | 34,178,188[97] | 14.3 | Algiers | |
| 7,492 | 2,118,519(2010) | 226.2 | Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Santa Cruz de Tenerife | |
| 20 | 71,505(2001) | 3,575.2 | — | |
| 1,001,450 | 83,082,869[97] total, Asia 1.4m | 82.9 | Cairo | |
| 1,759,540 | 6,310,434[97] | 3.6 | Tripoli | |
| 797 | 245,000(2001) | 307.4 | Funchal | |
| 12 | 66,411(2001) | 5,534.2 | — | |
| 446,550 | 34,859,364[97] | 78.0 | Rabat | |
| 619,745[97] | 8,260,490 [97] | 13.3 | Juba | |
| 1,861,484 | 36,787,012[97] | 19.7 | Khartoum | |
| 163,610 | 10,486,339[97] | 64.1 | Tunis | |
| 266,000 | 405,210[97] | 1.5 | El Aaiún | |
| Southern Africa | ||||
| 600,370 | 1,990,876[97] | 3.3 | Gaborone | |
| 30,355 | 2,130,819[97] | 70.2 | Maseru | |
| 390,580 | 11,392,629[97] | 29.1 | Harare | |
| 825,418 | 2,108,665[97] | 2.6 | Windhoek | |
| 1,219,912 | 49,052,489[97] | 40.2 | Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria[104] | |
| 17,363 | 1,123,913[97] | 64.7 | Mbabane | |
| Western Africa | ||||
| 112,620 | 8,791,832[97] | 78.0 | Porto-Novo | |
| 274,200 | 15,746,232[97] | 57.4 | Ouagadougou | |
| 4,033 | 429,474[97] | 107.3 | Praia | |
| 322,460 | 20,617,068[97] | 63.9 | Abidjan,[105] Yamoussoukro | |
| 11,300 | 1,782,893[97] | 157.7 | Banjul | |
| 239,460 | 23,832,495[97] | 99.5 | Accra | |
| 245,857 | 10,057,975[97] | 40.9 | Conakry | |
| 36,120 | 1,533,964[97] | 42.5 | Bissau | |
| 111,370 | 3,441,790[97] | 30.9 | Monrovia | |
| 1,240,000 | 12,666,987[97] | 10.2 | Bamako | |
| 1,030,700 | 3,129,486[97] | 3.0 | Nouakchott | |
| 1,267,000 | 15,306,252[97] | 12.1 | Niamey | |
| 923,768 | 158,259,000[97] | 161.5 | Abuja | |
| 410 | 7,637[97] | 14.4 | Jamestown | |
| 196,190 | 13,711,597[97] | 69.9 | Dakar | |
| 71,740 | 6,440,053[97] | 89.9 | Freetown | |
| 56,785 | 6,019,877[97] | 106.0 | Lomé | |
| Africa Total | 30,368,609 | 1,001,320,281 | 33.0 | |




















Thanks for sharing the best information, I am really enjoying reading your well written articles lube oil blending machine
ReplyDelete